Robotic ImagingAugust 23, 2022
The use of laser scanning services has taken over the AEC industry and rapidly transformed its processes. With the emerging integration of BIM and 3D laser scans, physical surveillance and inspection have been replaced by LiDAR drones and 3D laser scanning surveys.
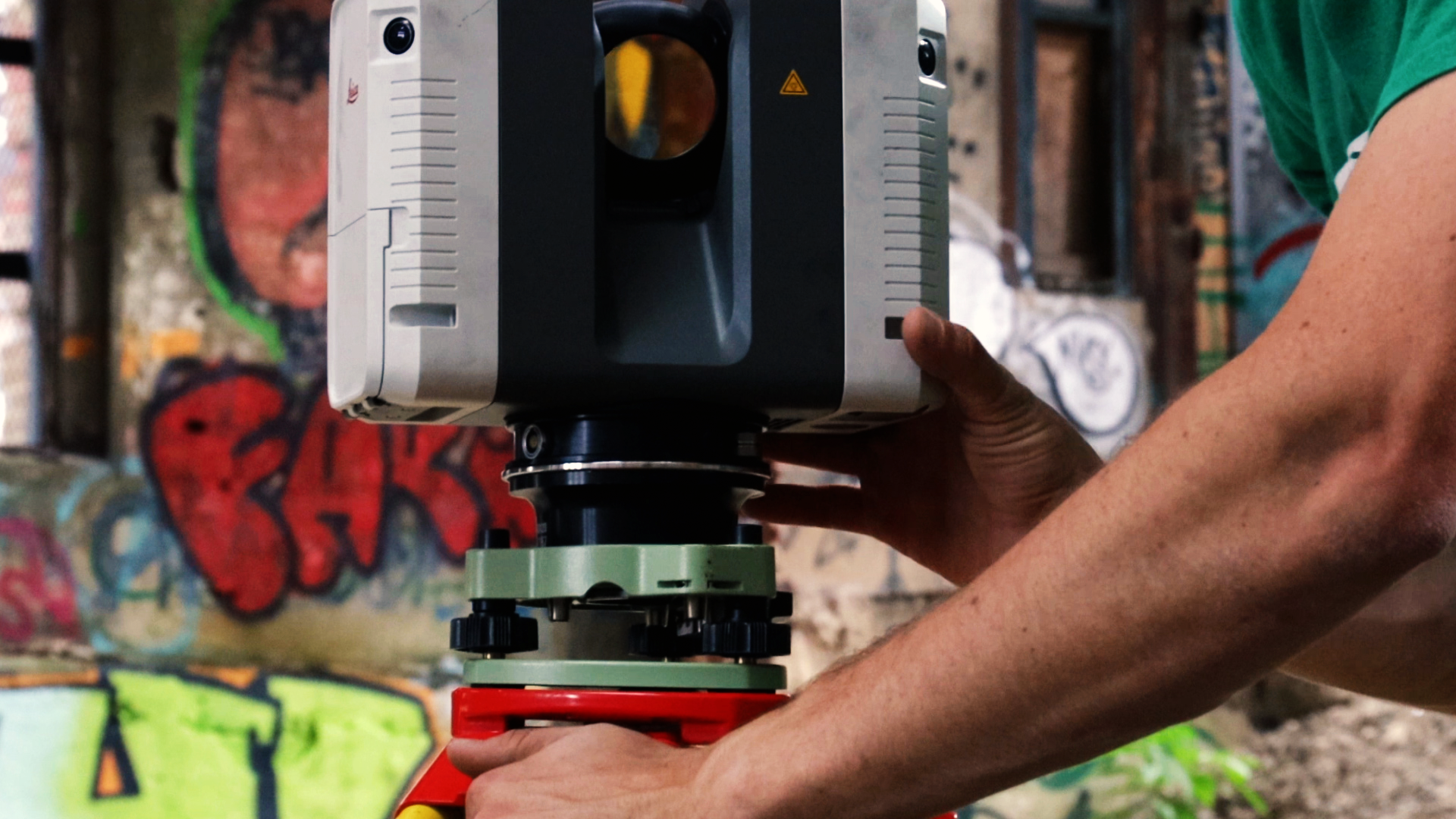
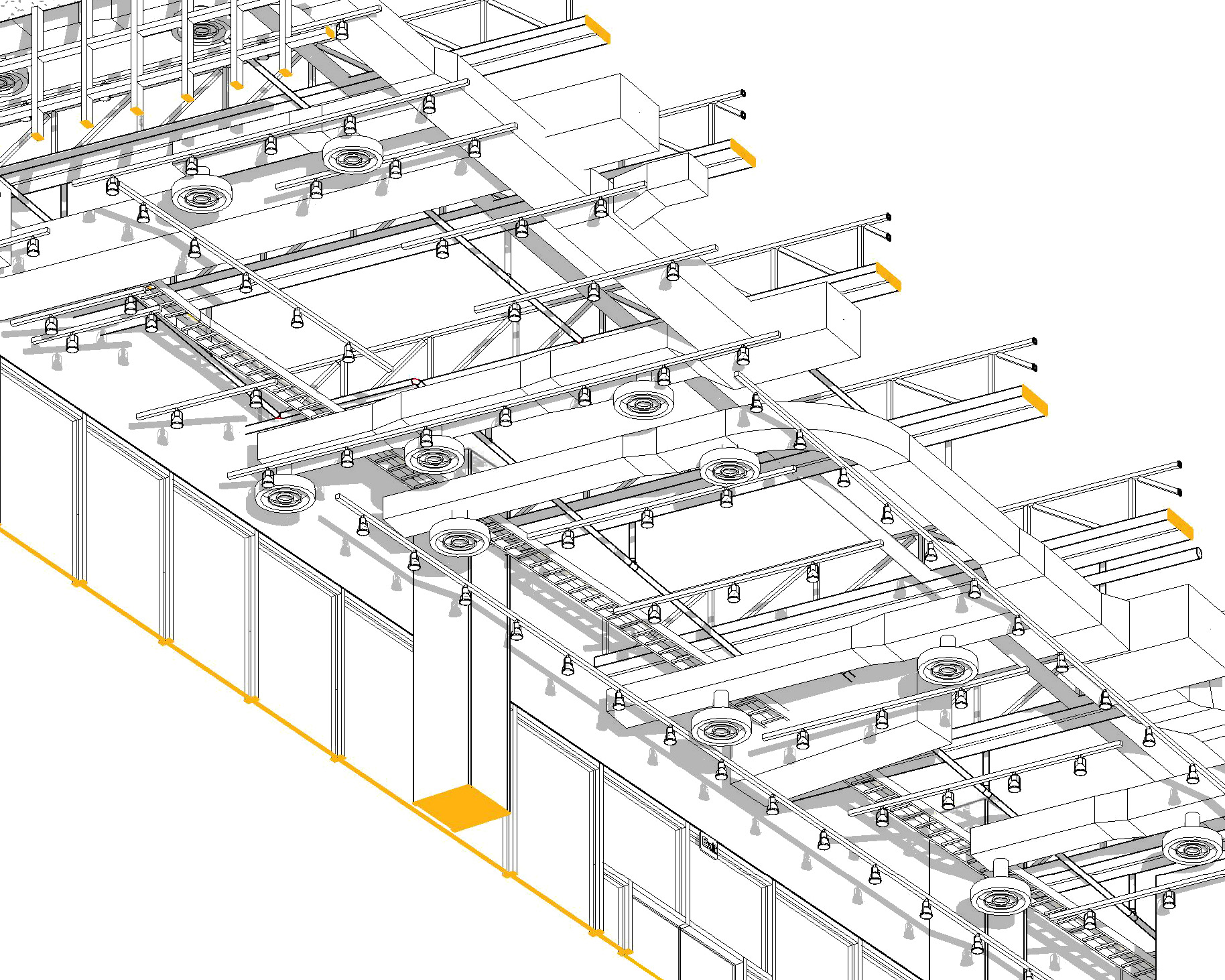
High-definition 3D laser scanning, also known as reality capture service, employs a technique where laser rays are used to collect data from a construction site. The laser beams measure intricate details of the structure, including the accurate dimensions of the building components and how each element is linked to the other. This technology is known as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging).
Suggested reading: If you want to learn more about how LiDAR scanning works, check out this article.
While 3D laser scanning took some time to arrive at the construction field, it has now become a widely accepted technique worldwide.
3D Scanning in Construction
Real estate 3D scanning services capture a three-dimensional image of an object in the form of a point cloud. This collected data is then used to build a 3D BIM model. Here are the steps of this process.
- Place the equipment at a point near the area to be scanned.
- Initiate the scanning process.
- The scanner collects data in the form of a point cloud to later be registered.
- Transfer the data to BIM software.
- Create an as-built / 3D BIM model through a software like Revit or AutoCAD using a point cloud underlay.
3 Types of 3D Scanners used in Construction
There are three major types of 3D scanners used in the construction industry, depending on their operational platforms.
- TLS (Terrestrial Laser Scanner)
TLS, also known as ground LiDAR, is an equipment that is mounted on a tripod in the area that needs to be scanned. Since the device stays stationary during the scanning process, its results are the most accurate among all other scanners available on the market.
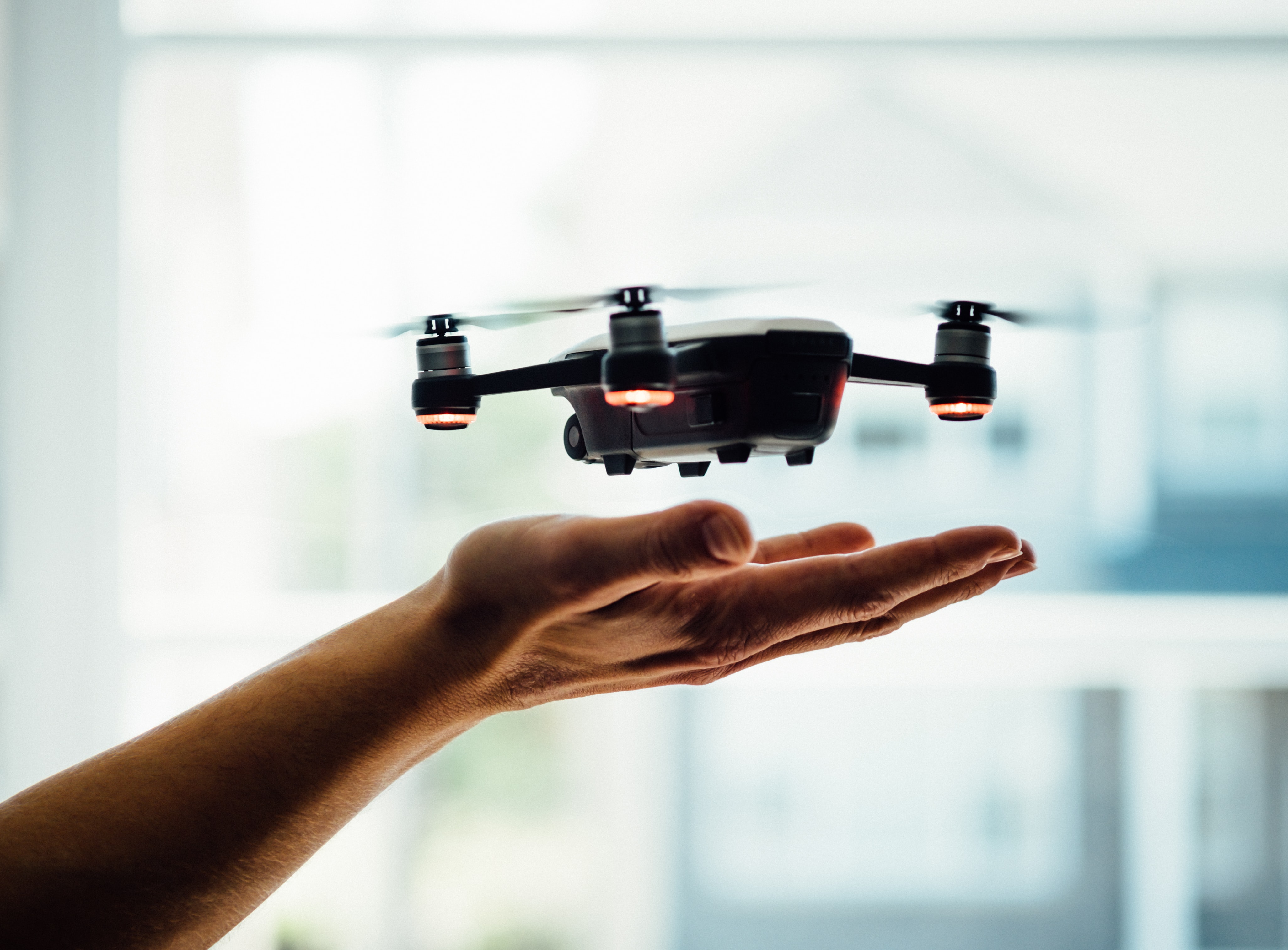
- ALS (Aerial Laser Scanner)
ALS is also known as aerial LiDAR, and this device is one that can be installed on an aircraft. As the aircraft moves, the scanner collects data from the on-ground site. The accuracy of aerial scanners is considerably low compared to others since it is constantly in motion. This scanner is better suited to mapping geographical features and topography.
- Mobile Laser Scanner
MLS or mobile laser scanners are relatively smaller in size and lighter than the other two. This scanner can be mounted on land-based vehicles such as trains, cars, and trucks, and this device can be widely used in autonomous vehicle sensing systems and 3D city mapping applications.
Application of 3D laser scanning in Construction
3D scanning services can be applied across various construction processes. Some of them are listed below:
- Construction designing
- Creating as-built drawings and models
- Surveying
- Calculating construction material
- Clash detection
- Renovation and rebuilding of structures
The biggest benefit by far is the enhanced coordination. Majority of our clients work directly with other consultants in the industry to best optimize their projects. By starting the project with a central, accurate model, the project starts on the right track. Scan-to-BIM eliminates the need for on-site visits, which are incredibly expensive and time draining. Laser scanning creates a 3D virtual overview and Matterport provides photogrammetry which combined eliminates the need for site visits. A project team has access to the smallest site details, to better understand the complexities present in the site.
While the construction industry has been quite slow in adopting new technology, the use of 3D laser scanners has become a top priority in construction projects for accurate and precise survey data. If you're not already benefiting from this technology, now is a good time to integrate it into your company's construction process.