Robotic ImagingApril 30, 2022
What is Laser scanning?
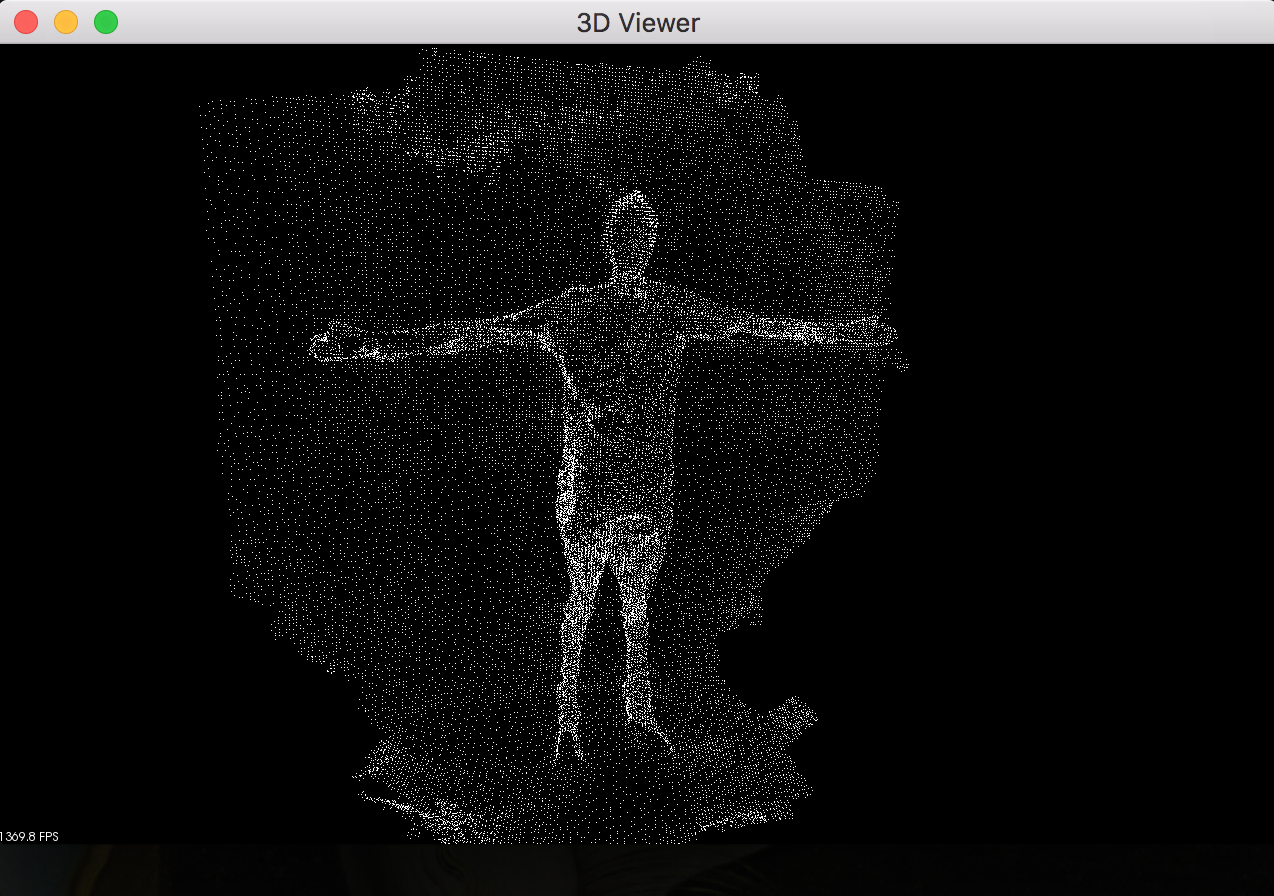
Laser scanning as a surveying method is used to generate complex models of land and buildings. It collects data points that accurately measure objects and buildings, and can be used in different kinds of models and simulations. Laser scanning uses cloud point data or 3D data points. These data points help engineers capture the detailed and accurate properties of an object. Scanning offers detailed information about an object’s size and shape, and allows that data to be transferred into a 3D digital model. The high level of detail and accuracy of laser scans allows engineers to create intricate and complex structure models without disrupting the site. Laser scanners can process massive amounts of data and easily share that data to help engineers and project managers design, visualize, and execute their projects.
How does it work?
First, laser scanners emit infrared light waves that reach out and touch the surrounding surfaces. Objects in the laser path then reflect the light back to the sensor. The sensor uses this information to determine how far away the object is. This is called, “time-of-flight” measurement. The time-of-flight measurement is calculated for every surface of the object. A laser scanner can collect millions of data points in just a few seconds. The distances measured on the structure are made into coordinates. When these coordinates are processed, they build a digital model of the spaces that were scanned. The model includes accurate dimensions, topographic features, and objects, providing a full scope of object data.
The evolution of laser scans
Laser scanning originated in the 1960s. Before their invention, land surveying was completed manually. Surveyors used tools like tape measures, plumb bobs, piano wire, and laser range finders. Surveying land could take weeks or months, depending on the size and complexity of the project. Manually collecting data often lead to errors and missing data, resulting in project issues and increased costs. Once laser scanners were introduced, the equipment consisted of lights, cameras, and projectors. During this time, the data was still manually processed. The introduction of LiDAR systems in 1985 changed the way data was collected. LiDAR systems used high-quality laser beams and shadowing to generate accurate and impactful data.
Suggested reading: If you want to learn more about BIM terminology check out this article.
How we use laser scanning
Laser scanning is utilized by many different industries, like construction, archaeology, and even medicine. Some of its other real-world applications are listed below.
- Historical preservation: Laser scanning documents the complexities of existing buildings and creates as-built models to preserve or restore them.
- Site surveying: Laser Scanners have the capacity to make volume calculations, topographic surveys, and as-built surveys.
- Archeology: Archeologists can also use point cloud data to discover hidden settlements underground. Point clouds provide data that can help find artifacts and new dig sites. Data can also help build digital replicas of discoveries.
- Designing prosthetics: Doctors and other medical professionals can use cloud point data to design highly accurate prosthetics for patients efficiently.
- Construction: Laser scanning provides a real-time, usable model of the project during every stage of the construction project. Models help guard against error and help project managers save money and time.
- Law enforcement: Laser Scanners are used in crime scene reconstruction, crime scene documentation, forensic investigations, fire incident analysis, and much more. Instead of manually documenting this information, laser scanning can save hours of documentation time and generate a digital replica of findings.
- Special effects: Hollywood also uses point cloud data to produce accurate special effects for movies and TV. Gaming companies are beginning to adopt this technology for video games we well.
- Security: Laser Scanners are used by security personnel to obtain data that can be used to save lives when reacting to potential threats.
- Insurance: Laser Scanners can document the actual state of a property. It can also accurately record damages.
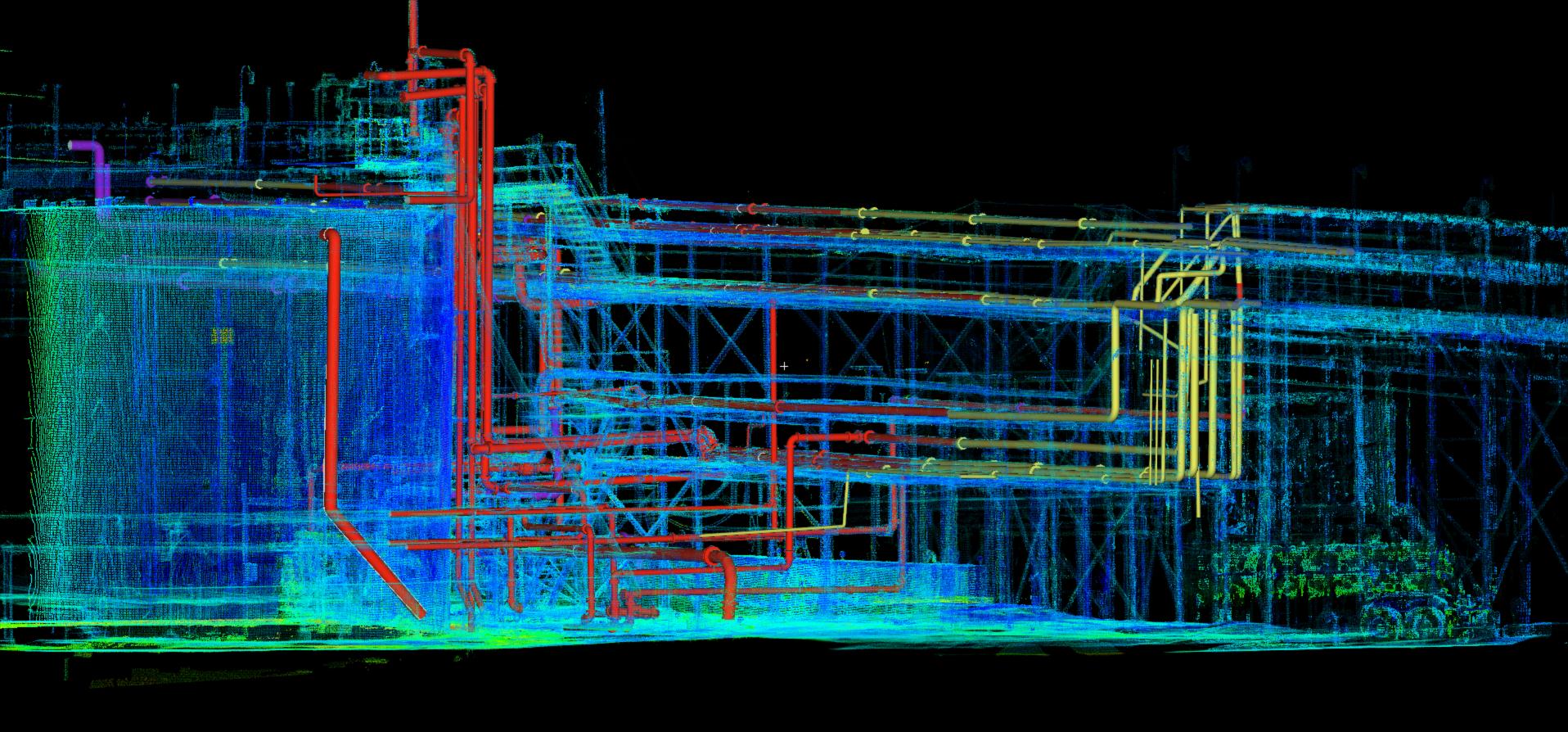
- Oil and gas: Laser scanning help the planning, engineering, and maintenance of oil platforms. They can avoid installation issues and errors by correctly modeling complex piping structures.
- Civil engineering: Laser Scanners capture accurate, as-built data from existing buildings and help engineers develop precise design plans.
- Facilities management: Laser scanning offers models of complex factories, which are helpful when maintaining facilities